What Is the Success Rate of Bariatric Procedure?
Bariatric surgery, known as weight loss surgery, can be a very effective method to lose excess Weight. But it’s important to understand that there is more to long-term weight loss than just a surgical procedure. A person’s plan to manage obesity and the health-related problems that accompany it can be very complicated and involved.


Here’s a summary of its key goals:
- Promote Significant Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery is the most effective method for achieving lasting, substantial weight loss for people with severe obesity.
- Improve Overall Health: By promoting weight loss, bariatric surgery can significantly reduce the risk of various obesity-related health problems, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea, and fatty liver disease.
- Manage Obesity-Related Health Conditions: In some cases, bariatric surgery can help manage or reverse existing type 2 diabetes.

Bariatric procedure is the start of a long-term weight loss plan that will hopefully address and resolve accompanying illnesses like diabetes or high blood pressure. However, what is the actual long-term success rate of gastric bypass surgery? And for those who were successful, or those who had Weight regain, what happened or didn’t happen on their weight loss surgery journey?
Those are some questions we will find out in this article so you can better understand these surgeries and the care they imply.
Bariatric surgery success rates


The success rate of bariatric surgery will vary depending on several factors, beginning with the type of surgery performed, the patient’s overall health, and their adherence to post-operative guidelines, including creating a new lifestyle, healthy diet, and physical activity.
How is the success rate measured?
Success is generally measured by the amount of weight loss achieved, improvement in obesity-related health conditions, and overall quality of life after surgery. Here are some focus points regarding the success degree of bariatric surgery:


- Weight Loss: Bariatric surgery can lead to relevant weight loss in most patients. On average, obese patients can loose 60-80% of their excess body weight in the first two years after surgery. However, these results can vary.
- Improvement in Obesity-Related Diseases: Bariatric surgery is often effective in improving or resolving obesity-related comorbidities such as sleep disorders, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and joint pain. The extent of improvement can vary among patients.
- Quality of Life: Many bariatric surgery patients experience an enhanced quality of life after the procedure. bariatric surgery. This can include increased mobility, higher self-esteem, better mental balance, and a reduced risk of obesity-related complications.
- Complications and Risks during Bariatric Surgery: Like any surgery, bariatric surgery carries risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Bariatric surgery Lasting Success: Success after bariatric surgery depends on factors like eating habits, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Patients who adhere to recommended post-operative dietary guidelines, attend follow-up appointments and make sustainable lifestyle changes are more likely to sustain weight loss, and experience long-term success.
It’s essential for individuals considering bariatric surgery to consult with a healthcare provider specializing in weight management and undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine if they are suitable candidates for surgery. Additionally, ongoing support, follow-up care, and lifestyle modifications are crucial for accomplishing and maintaining successful outcomes after bariatric surgery.
What is the long-term bariatric surgery success rate?
The long-lasting success rate of weight loss procedure is between 68% and 74%, and studies have demonstrated that the favorable effects on weight loss are sustained for up to 20 years after roux-en-Y gastric bypass, of course, to achieve this, bariatric patients may require bariatric revisions. This means that most patients maintain 50-75% excess weight loss, with an average patient remaining at least 100 pounds. Weight loss surgery patients typically lose the most Weight 1–2 years after their bariatric surgery and see substantial weight improvements in obesity-related conditions.
What percentage of bariatric surgeries fail?


One standard measure of success in bariatric surgery is achieving and maintaining substantial weight loss. Research and clinical studies have shown that many patients experience successful weight loss following bariatric surgery.
For example, a study published in PubMed named Nutrition Care for Patients with Weight Regain after Bariatric Surgery mentions that approximately 20–30% of patients do not accomplish successful weight outcomes, and bariatric patients may experience a regain of 20–25% of their loss weight after an initial period of weight loss.
Another article published in JAMA Surgery in 2020 found that 65-75% of patients achieved at least 50% excess weight loss after bariatric surgery.


We need to mention these so you can have all the considerations and know in advance that the surgery is a great solution. Still, as a bariatric patient, there are routines that you need to change to have a lasting transformation and to have a successful outcome.
Refrain from being frustrated if the outcome differs from what you expected, mainly because some factors affect this situation.
Ways to measure the success of bariatric surgery procedures


The success or failure of bariatric procedures can be assessed in various ways, including weight loss failure, obesity-related medical conditions, and overall improvement in quality of life. The success rates of bariatric surgeries can fluctuate based on several aspects like the kind of surgery, patient characteristics, and follow-up care.
The percentage of bariatric procedures considered “failures” can change depending on the criteria used to define failure and the duration of follow-up. Here are some general insights based on different measures of failure:
- Unsuccessful Weight Loss: If failure is defined as not achieving a certain percentage of excess weight loss (EWL) after surgery, studies have reported failure rates ranging from about 10% to 30%. However, these rates vary widely depending on the surgical procedure, patient characteristics, and follow-up duration.
- Complications and Revisions: The rate of surgical complications that may require revision surgery is typically lower, shifting from 1% to 20%, depending on the surgical team’s procedure and expertise. Revision surgeries are sometimes necessary due to complications or inadequate weight loss.
- Significant Weight Regain: Weight regain after successful weight loss is a common concern. Studies suggest that a considerable percentage of patients may experience some degree of Weight regain over the long term, although the exact percentage varies widely.
- Patient Satisfaction and Quality of Life: bariatric patient satisfaction are generally high, with many patients reporting significant improvements in obesity-related comorbidities, such as cardiovascular risk factors, and overall well-being.
However, it’s essential to note that success rates can vary among different surgical procedures. For instance, gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy generally have higher success rates than adjustable gastric banding procedures. Also, long-lasting success often depends on lifestyle changes, dietary habits, and ongoing medical follow-up.
While bariatric surgery could be highly effective for weight loss and improving health outcomes in many patients, the definition of “failure” can also vary.
Some patients who underwent bariatric surgery may not acomplish their desired weight loss goals or may experience complications post-surgery, which could be considered as “failure” in specific contexts. Therefore, it’s crucial for patients considering bariatric surgery, to recognize the downside risks, benefits, and expected outcomes based on their circumstances.
What is the long-term gastric bypass success rate?
Ninety-three percent of gastric bypass surgery patients sustained at least a 10 percent weight loss from their baseline, 70 percent kept 20 percent weight loss, and only 40 percent sustained at least a 30 percent weight loss after 12 years, according to a long-term study of patients who had undergone gastric bypass.
While not perfect results, many who underwent weight loss procedures managed to keep a good percentage off. Gastric bypass surgery is recognized too as the “gold standard bariatric operation” for weight loss, but there is still a chance you could experience Weight regain.
Why is bariatric surgery performed?
This bariatric surgery is a weight loss procedure that address severe obesity who are morbidly obese, typically classified as class III with a body mass index more significant than 40 or a body mass index greater than 35 with at least one obesity-related illness.
Bariatric surgery aims to help the patient achieve long-term weight loss when diet and exercise haven’t been successful in achieving sufficient weight loss. Also, they help decrease the risk of obesity-related comorbidities or diseases, such as:
- diabetes
- high blood pressure
- hypertension
- cardiovascular disease
- stroke
- sleep apnea
- gout
- heart disease
These weight loss surgeries aim to help severely obese patients lose excess Weight and reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening weight-related health problems. One of the most common weight loss surgery is gastric bypass surgery.
Read More Weight Loss Surgery FAQs
What is gastric bypass surgery?
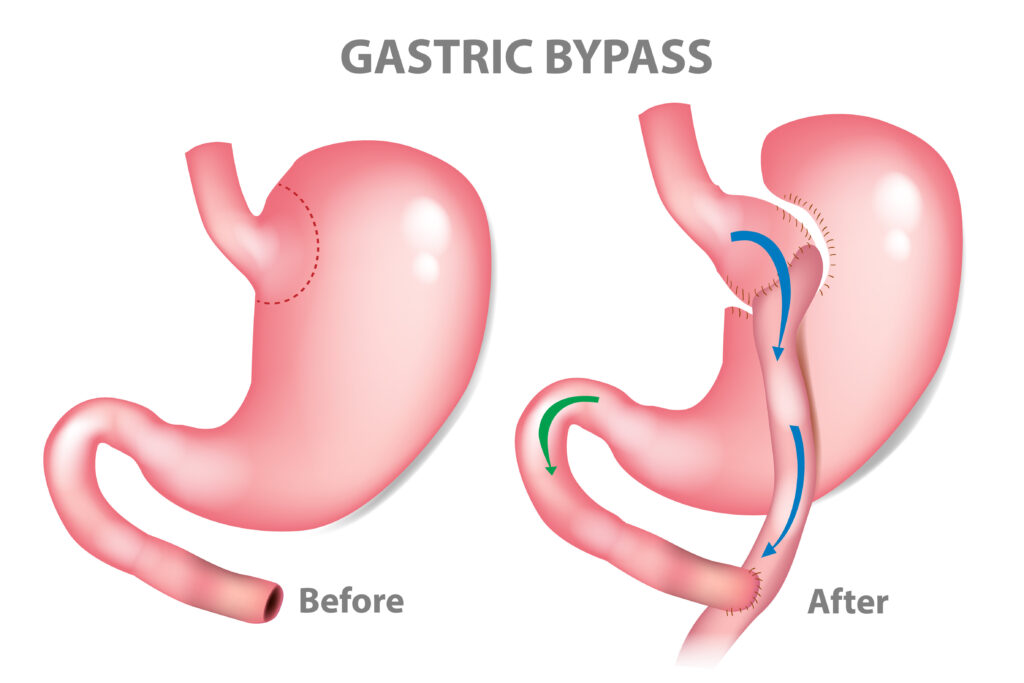

Roux-en-Y gastric bypass procedure is a weight loss surgery where a smaller stomach bag is created from your stomach to help the patient lose Weight. The gastric bypass surgery works by changing the stomach and small intestines’ anatomy (or position). The smaller stomach is connected straight to the middle section of your small bowel, which allows food to bypass large parts of your stomach and duodenum, where nutrient absorption typically occurs.
This weight loss surgery helps limit calorie intake by increasing food intake restriction due to less upper GI space and decreasing caloric absorption. The new stomach position and size change the appetite, satiety (feeling full), and metabolism (how your body burns calories), all of which can help the patient lose Weight.
How gastric bypass surgery can be performed?

It can be performed laparoscopically, actually laparoscopic gastric bypass (RYGB) is the most common type of bariatric surgery, a minimally invasive surgery performed to help patients with severe obesity lose weight. In this surgery, the surgeon creates a small pouch out of the upper portion of the stomach, about the size of an egg.
The small intestine is then divided into two sections. One section is connected to the new pouch, and the other section is connected further down the small intestine. This bypasses a portion of the small intestine, which reduces the amount of nutrients and calories that are absorbed by the body.
What are the Gastric Bypass Success Rates
Gastric bypass surgery has a relatively high success degree for weight loss, but it’s important to understand how “success” is defined. Here’s a breakdown:
- Overall Weight Loss: On average, the vast majority of patients may achieve weight loss ranging from 60% to 80% of excess weight.
- Lifelong Weight Loss: While the initial weight loss is impressive, sustained weight loss requires commitment to prevent weight regain. Around 20-25% of patients may experience weight regain after a few years.
- Health Improvements: Beyond weight loss, roux en y gastric bypass can significantly improve obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and fatty liver disease.
Gastric bypass procedure & diseases
It isn’t only the BMI that an excess weight loss surgery can positively affect, but it can also completely eradicate any dangerous diseases. A study was done on patients 12 years after weight loss surgery and it indicated incredible durability of weight loss, effective remission, and prevention of hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. The effect gastric bypass has on diseases that existed before the surgery has a positive correlation to the after-effects of weight loss.
Long-term gastric bypass surgery is effective at improving these obesity-related conditions. Also, gastrointestinal hormones play a large role in the regulation of hunger and satiety. With gastric bypass, the surgery changes the action of specific hormones, such as ghrelin or the “hunger hormone.” Those who have gastric bypass surgery have lower ghrelin levels than those who lose weight naturally, and this feeling of “fullness” or satiety is long-term.
If you’re considering Roux en y gastric bypass surgery, it’s important to consult with a doctor specializing in bariatric surgery to discuss the potential benefits and risks involved. They can assess your individual situation and determine if you’re a good candidate for this type of surgery.
Mental health & gastric bypass surgery
While the physical effects of weight loss surgery are often noticed first, the mental effects can also change the surgery’s long-term effectiveness. According to this study, the most common mental health conditions of patients seeking gastric bypass surgery were depression and binge-eating disorder. While post-op data about eating disorders was inconclusive, the weight loss surgery data shows substantial numbers that showed a decrease in patients with depression and the severity of depressive symptoms.
While some studies indicate positive correlations, others show different data. According to this study, the lifelong success rates can be as low as 50%. With low numbers due to not the actual surgery itself but psychological issues post-op. Patients who have several additional health conditions or who had pre-existing mental health problems before their surgeries were less likely to do well after surgery than those with only one disease state (obesity).
It’s important to note that a positive mental attitude and an approach to healthy living after weight loss surgery can contribute to keeping excess Weight off for good.
What is Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy, also called vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG), is a laparoscopically bariatric procedure to aid weight loss in patients with severe obesity. Unlike gastric bypass, it doesn’t involve rerouting the intestines.
Sleeve gastrectomy works primarily by restricting the amount of food you can eat. The smaller stomach pouch fills up quicker, leading to earlier feelings of fullness and reduced calorie intake. The surgery may also influence gut hormones that regulate hunger and satiety.
What is the degree of success of sleeve gastrectomy?
- Excess Weight Loss: In the first year, the degree of success is vast, with most patients losing 60-70% of excess Weight.
- Long-Term Weight Loss: Sustained weight loss requires a lifestyle transformation to prevent regain Weight. Around 20-25% of patients may experience Weight regain after a few years.
- Health Improvements: Beyond weight loss, sleeve gastrectomy can significantly improve obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep disorders, and fatty liver disease.
What is Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding?
Also commonly referred to as a lap band or adjustable gastric band, it is a type of weight loss surgery performed to aid weight loss in patients with severe obesity.
Unlike other bariatric surgeries, it involves placing an adjustable band around the top part of the stomach rather than removing or rerouting parts of it.
The adjustable gastric banding restricts the amount of food passing from the small pouch into the lower stomach, leading to earlier feelings of fullness and reduced calorie intake. The band can be further adjusted by injecting saline solution through the access port, making the band tighter and further restricting food passage.
What is the success rate of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding has the following success degree:
- Overall Weight Loss: around 50% of patients achieve a significant weight loss of 30-50% of their excess body weight within two years after Lap-band.
- Long-Term Weight Loss: Sustaining weight loss is challenging. Up to 70% of patients may experience Weight regain or require the band’s removal after ten years.
- Health Improvements: LAGB can improve obesity-related conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep disorders, etc, but the improvements may not be as significant as with other bariatric surgeries.
Managing lifestyle changes after weight loss surgery
We discussed earlier that weight loss surgery is the first step to long-term excess weight loss success. Those who have successfully kept their excess Weight off and maintained a healthy lifestyle after surgery have made major changes in how they eat and live.
Successful bariatric surgery patients understand that gastric bypass is a lifelong commitment and not just something they do for themselves right now. They find ways to stay active by engaging in enjoyable physical activities like walking or exercising and are incredibly mindful of how and when they eat. Keeping up with the physical and nutritional part of the gastric bypass surgery is a key element to keeping the excess Weight off – for good.
DR. GABRIELA RODRIGUEZ RUIZ MD Ph.D. FACS

