What men need to know about gynecomastia surgery
Gynecomastia, what are its causes, and what you can do about it
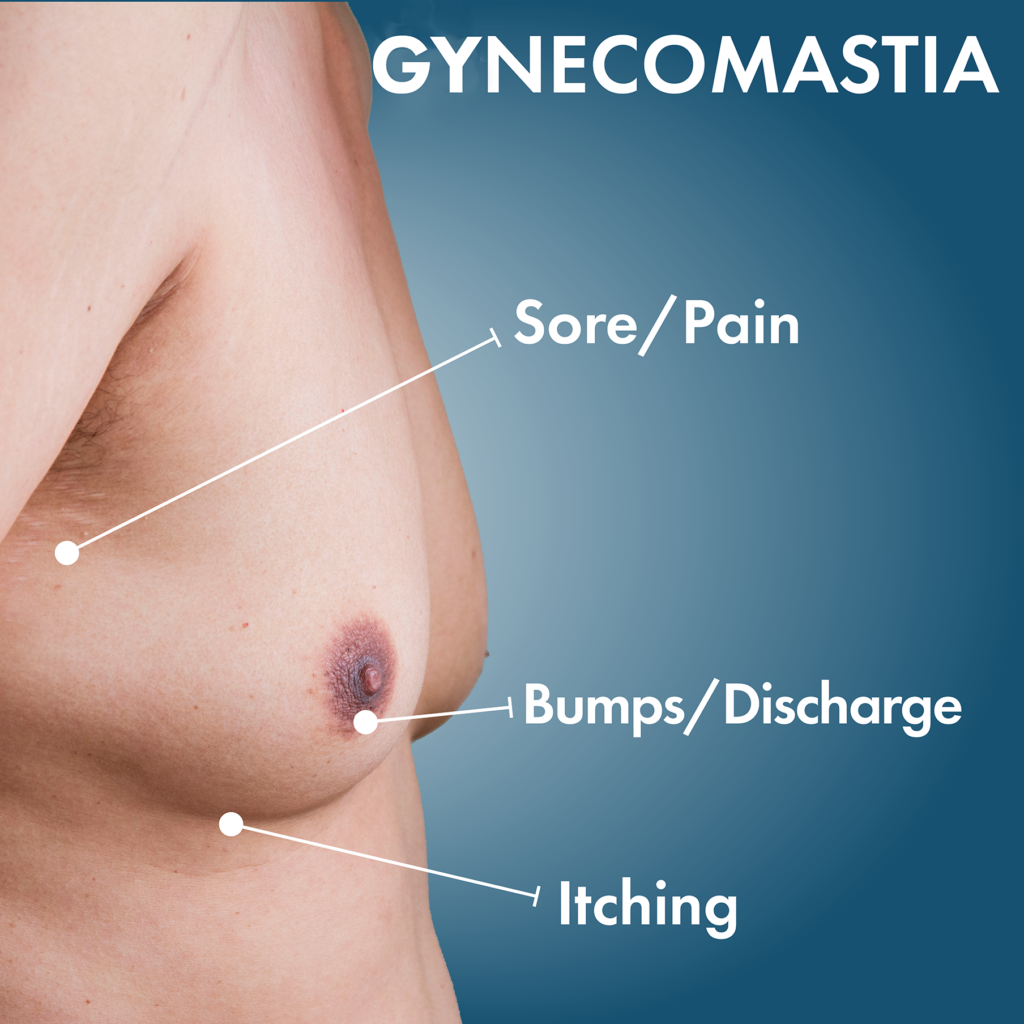

Boys or men who have gynecomastia experience enlargement of the glandular tissue in their breasts, which can occasionally be uncomfortable or tender around the nipple. It typically happens in infancy, adolescence, or middle to late life and is the result of a hormonal imbalance. It’s important to distinguish between gynecomastia and breast enlargement brought on by fat deposits in overweight men.
The medical term for enlarged male breasts is gynecomastia. Teenagers going through puberty frequently experience this condition. By the age of 21, it naturally disappears for many young men. Gynecomastia in adult males is uncommonly treatable with medication, exercise, and diet on their own. Hormone imbalances, use of anabolic steroids, marijuana use, and some medications are the main causes of gynecomastia.
The most prevalent male breast disorder is gynecomastia. Around the world, 50 to 65 percent of boys and men are affected. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, and it occasionally appears unevenly. Adult men with gynecomastia frequently feel helpless about their condition. Gynecomastia is treatable, which is good news. Most teenage boys with enlarged breasts will see it go away by the time they’re adults.
Losing weight and exercising may help men with fatty gynecomastia. Gynecomastia typically consists of extra fibrous breast tissue that does not respond to do-it-yourself treatments. Gynecomastia surgery for male breast reduction will completely and permanently cure this type of gynecomastia.
Causes of gynecomastia and excess breast tissue in men
People of both sexes produce both types of hormones, despite the common misconception that androgens (like testosterone) are “male hormones” and estrogens are “female hormones.” While estrogen is also present, androgens are by far the most prevalent hormone in males.
When the ratio changes, either by a rise in estrogen or a fall in androgens, gynecomastia can result. This can happen because of using certain medications or herbal remedies, hormonal changes associated with puberty or aging, or other factors.
Male breasts may persist without medical intervention or surgical treatment if gynecomastia is caused by specific drugs or substances. Exercise has already been shown to be ineffective in reducing male breast tissue, but male breast reduction can be a great way to successfully correct gynecomastia by getting rid of extra fat and glandular tissue while giving the chest a flatter appearance.
How does gynecomastia develop?
Gynecomastia is frequently brought on by an imbalance of the hormone’s estrogen and androgen. The hormone that regulates breast growth, estrogen, is typically only produced in small amounts by men’s bodies. Your breasts may enlarge if your body produces too much estrogen or if you have low testosterone (hypogonadism). Due to extra fatty tissue, enlarged breasts can occasionally develop in obese people. Pseudo gynecomastia is the name for this condition.
Gynecomastia Surgery: Men & Breast Reduction
If desired, male breast reduction can also treat swollen, enlarged, or puffy nipples, allowing patients to fully enjoy life without feeling self-conscious about having male breasts. The best way to get rid of excess breast tissue is through gynecomastia surgery. A flat and more sculpted chest will be yours after a male breast reduction procedure.
Gynecomastia surgery is a relatively simple procedure that, depending on your case, uses methods like surgical excision and liposuction to create more masculine chest contours and remove excess breast tissue. To minimize the amount of post-surgical scarring as much as possible, our skilled plastic surgeons are very meticulous in making small incisions.
How long does Gynecomastia recovery take?
Most patients leave the hospital the same day. Most patients go back to work soon after surgery, and for 4 to 6 weeks they wear a compression garment to reduce swelling and hasten recovery. Following your surgeon’s aftercare instructions and a close follow-up appointment, as with any surgical procedure, guarantees ideal results and a speedy recovery.
Diagnosing Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is identified by medical professionals through questioning and physical examination. Other tests are rarely required, but occasionally blood tests are.
Treatment for Gynecomastia & Male Breast Reduction Surgery
Gynecomastia typically disappears on its own without medical intervention. Within a few months to a couple of years, the breasts flatten out. Some medications can help to correct gynecomastia if it is very severe. Gynecomastia can also be surgically treated to shrink the breasts if it persists after puberty.
There are six forms of gynecomastia after years of study and experience:
- Type 1: Only the nipple/areola area has extra tissue. A tight and straight lateral chest fold can be seen.
- Type 2: Breast tissue crosses the fold in the chest. The lateral chest fold is rounded and tightly formed.
- Type 3: Extending breast tissue that folds across. The lateral chest fold is horizontal and exhibits little flexibility.
- Type 4: The axilla and breast tissue are connected. In front of the armpit, there is a little breast roll known as the lateral chest fold.
- Type 5: The axilla contains breast tissue. A breast function that reaches the back of the armpit is known as the lateral chest fold.
- Type 6: The axilla contains breast tissue. A breast roll that wraps over to the back is called the lateral chest fold.
Gynecomastia is a disease that can be managed. There is no justification for dwelling on how your chest looks. No more concealing yourself in loose clothing. No more feeling uneasy in private settings. No more donning shirts at the beach or pool. Your overall well-being depends on practicing self-care. Start right away! Learn more about Gynecomastia and what you can do about it, visit our website at VIDA Wellness and Beauty and book your consultation today!